Телескопы Bresser Refractor 90 900 NG - инструкция пользователя по применению, эксплуатации и установке на русском языке. Мы надеемся, она поможет вам решить возникшие у вас вопросы при эксплуатации техники.
Если остались вопросы, задайте их в комментариях после инструкции.
"Загружаем инструкцию", означает, что нужно подождать пока файл загрузится и можно будет его читать онлайн. Некоторые инструкции очень большие и время их появления зависит от вашей скорости интернета.
EN
15
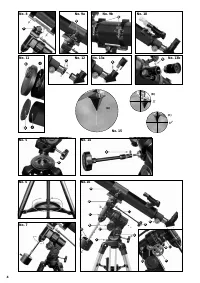
6. Finder scope
Your telescope is now roughly aligned and set.
To arrive at a comfortable observation position, carefully undo the
main tube mounting screws (No. 9, X) until you can rotate the tel-
escope's main tube. Move the eyepiece and finder scope/LED finder
scope until the position is comfortable for you.
Fine adjustment is done with the aid of the finder scope. Look
through the finder scope and try to align it with the North Star (No.
27) in the centre of the crosshairs (No. 31). In precisely adjusting
your telescope, you will find the shaft (No. 16, K) of the right ascen-
sion axis (No. 16, b) and that (No. 16, E) of the declination axis (No.
16, a) helpful.
7. Observation
Once you have found the North Star with your finder scope/LED
finder scope, you will be able to view it through your telescope eye-
piece.
If necessary, you can, with help of the flexible handles, align the
star more exactly, just as you can adjust the definition by using the
focusing wheel (No. 16, B).
Furthermore, you can now, by changing the eyepiece, increase the
magnification. Note that the magnification of the stars can hardly be
seen.
NOTE
Eyepieces enlarge the picture of the telescope's
prime focus. The less the eyepiece's focal lengths
is, the stronger the magnification is.
Various eyepieces are needed to reach different
magnifications. Begin every observation with a
low-powered magnification (20 mm eyepiece).
i
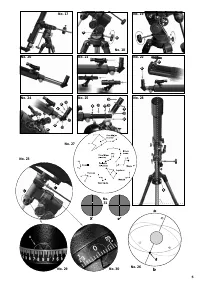
8. Find a star:
Initially, it may be difficult for you to find your bearings in the sky,
since the stars and constellations are constantly moving, and
according to season, date and time, their positions in the sky will
change. The North Star is the exception. It is a fixed star and the
starting point for all star maps.
When you first begin to observe the night sky, look at some well-
known constellations and star groups that are visible year-round.
This will help you to orient yourself and learn the functions of your
telescope.
If you have aligned your telescope accurately on one of these stars,
you will find that it vanishes from your visual field after a few minutes
due to the Earth's rotation. To even out this effect, you must turn the
flexible handle (No. 16, K) of the right ascension axis, and your tel-
escope will follow the trajectory of this star.
9. Part circles:
Stars and other celestial bodies are positioned in the sky by coordi-
nates. The place of a star is fixed in the universe by its right ascen-
sion and declination coordinates, similar to latitude and longitude on
Earth.
Declintion (No. 16, C) is the spacing of a celestial body from the
sky's equator, in angle degrees. To the north of the equator, the
degree number is positive. To the south of the equator, the degree
number is negative.
Right ascension (No. 16, M) is the measured distance of a star from
the sky's equator in sidereal (star) time. The vernal equinox is the
point where the ecliptic meets the equator (No. 26, e) at the begin-
ning of spring. The value of the daily celestial revolutions is counted
in the tempo of a 24-hour clock.
For more accurate information about this topic, consult star maps
and other literature, or the Internet.
10. Accessories
Your telescope is supplied with a number of accessories (No. 2).
Depending on your telescope's model, these accessories may
include the following:
10.1. Eyepieces
Change eyepieces to change your telescope's magnification.
700 mm
÷
20 mm
=
35X
700 mm
÷
12.5 mm
=
56X
700 mm
÷
4 mm
=
175X
Formula for calculating magnification:
Focal length (Telescope) ÷ Focal length (Eyepiece) = Magnification
Examples:
10.2. Zenith mirror (refraction telescope only)
The zenith mirror (No. 2, 19) reverses the image you see, and is
therefore used only for celestial observation.
10.3. Inversion lens
To see a vertical image the right way up, an inversion lens may be
used.
Loosen the clamping screws (No. 25, X) and remove all accesso-
ries from the eyepiece supports (No. 1, 6). Insert the inversion lens
(No. 2, 20) straight into the eyepiece supports and hand tighten the
clamping screws. Then insert the eyepiece (e.g. f=20 mm) into the
inversion lens opening and tighten the clamping screws (No. 25, Y).
10.4. Barlow lens
A Barlow lens increases magnification by a factor of three.
10.4.1 Assembling and using with refracting telescopes
If you use a refracting telescope, the Barlow lens should only be
inserted into the zenith mirror (No. 13a, X). Remove the eyepiece
from the zenith mirror and replace it with the Barlow lens. Then insert
the eyepiece with the greatest focal length and hand tighten the
clamping screws to affix it in place (No. 24).
10.4.2 Assembling and using with reflecting telescopes
If you use a reflecting telescope, loosen the clamping screws on the
eyepiece supports (No. 13b, X), and remove the eyepiece from those
supports. Then insert the Barlow lens straight into the supports and
hand tighten the clamping screws. Finally, insert the eyepiece with
the greatest focal length into the Barlow lens, and then fasten it in
place with the clamping screws (No. 24).
11. Dismantling:
After an interesting and successful observation, it is recommended
that you store the entire telescope in a dry, well-aired area.
On some telescopes, the tripod and mount can easily be separated.
The adjustments to the mount will remain intact.
Don't forget to put the dust-protection caps onto the tube
opening and onto the eyepiece connection before storing. Also, you
should stow all eyepieces and optical accessories in their
corresponding receptacles.
NOTE
The erecting lens is not recommended for ast-
ronomical observations. Only use the diagonal
mirror for astronomical observations. Use the
erecting lens to observe landscapes.
i
Notes on cleaning
Clean the eyepieces and lenses only with a soft, lint-free cloth, like
a microfibre cloth. To avoid scratching the lenses, use only gentle
pressure with the cleaning cloth.
To remove more stubborn dirt, moisten the cleaning cloth with an
eyeglass-cleaning solution and wipe the lenses gently.
Содержание
- 2 Руководство по эксплуатации; Never attempt to observe the sun with this telescope.; держать в недоступном для детей месте из-за опасности удушения.
- 43 Общая информация; Общее предупреждение; Комплектация может изменяться в зависимости от модели.; Часть 1 — Сборка
- 44 Лоток для аксессуаров; Сборка искателя / Искатель с красной точкой; Настройка искателя; Ручки тонких движений
- 45 Часть 2 — Использование; Установка полярной оси
- 46 Уход; Возможные объекты наблюдения; Устранение проблем
- 47 Гарантия и продление гарантийного срока